Satellite Internet: Bridging the Global Connectivity Gap
Satellite internet technology has emerged as a vital solution for extending digital access to regions where traditional terrestrial infrastructure, like fiber optic cables or cellular networks, is impractical or unavailable. By leveraging satellites orbiting Earth, this technology bypasses geographical barriers, offering a pathway to internet connectivity for remote communities, rural households, and even mobile platforms. It plays a crucial role in reducing the global digital divide, ensuring more people can participate in the interconnected world.
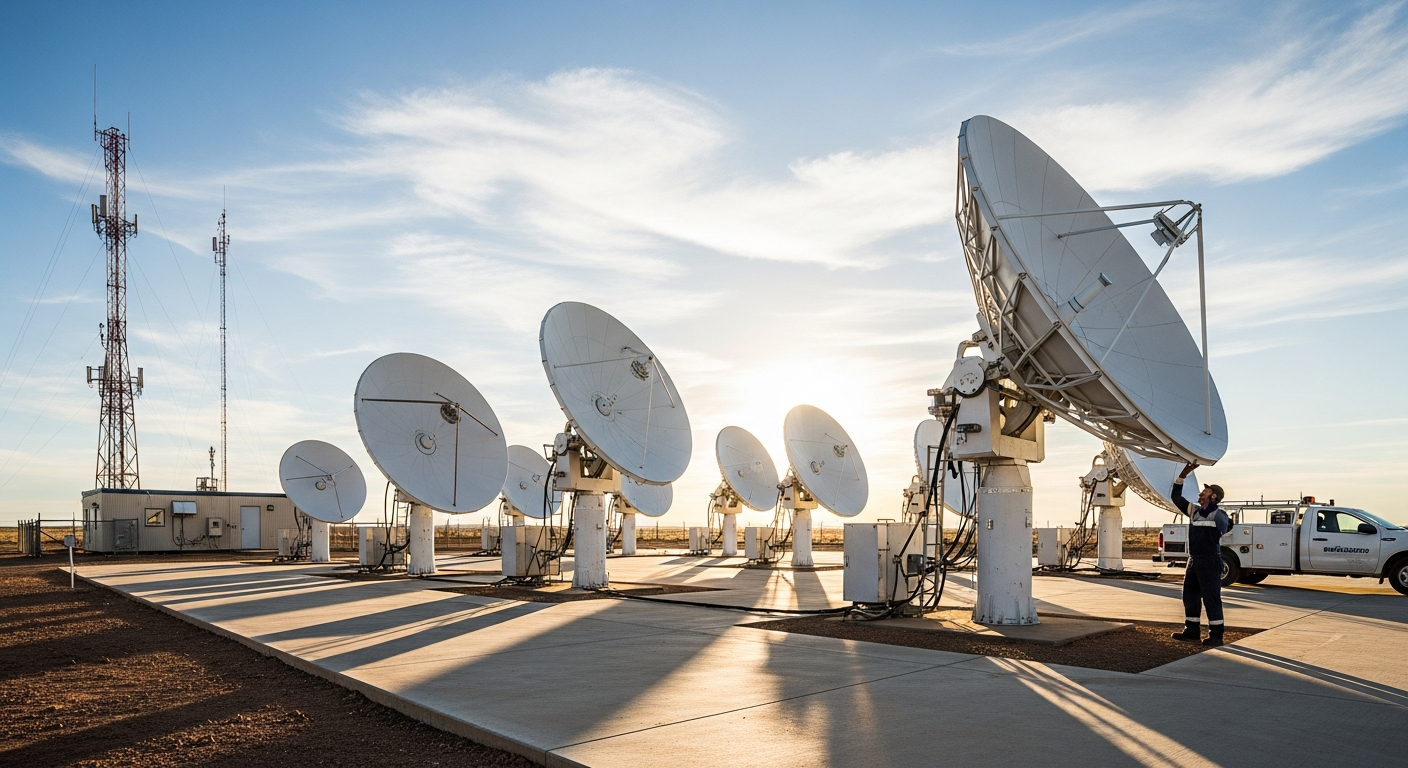

Understanding Satellite Internet Technology
Satellite internet operates by transmitting and receiving data through satellites positioned in Earth’s orbit. A user’s dish sends and receives signals to and from a satellite, which then relays these signals to a ground station connected to the broader internet. This communication system enables internet access in vast geographical areas, overcoming the limitations of physical cables. The technology relies on a sophisticated network of ground stations, orbiting satellites, and user terminals, making it a complex but effective solution for widespread digital communication.
Expanding Global Connectivity and Digital Access
One of the primary advantages of satellite internet is its capacity to extend internet access to underserved populations worldwide. In many rural and remote areas, the cost and logistical challenges of deploying traditional broadband infrastructure are prohibitive. Satellite technology offers a viable alternative, providing essential connectivity that supports education, healthcare, economic development, and social communication. This global reach helps to bridge the digital divide, empowering communities that might otherwise remain isolated from the digital economy and information resources.
How Does Satellite Internet Affect Network Performance and Speed?
The performance of satellite internet has seen significant advancements, particularly with the introduction of low Earth orbit (LEO) constellations. While earlier generations of geostationary satellites often had higher latency due to the greater distance signals had to travel, LEO satellites are closer to Earth, resulting in reduced latency and improved speeds. This innovation has made satellite internet a more competitive option for various applications, from streaming content to supporting remote work, offering a more responsive internet experience than previously possible. Data throughput capabilities continue to evolve, enhancing the overall user experience.
Ensuring Security and Reliability in Satellite Communication Systems
Security is a critical consideration for any internet service, and satellite communication systems are no exception. Providers implement various encryption and authentication protocols to protect user data and ensure the integrity of the network. While the nature of wireless transmission presents unique challenges, continuous innovation in security measures aims to safeguard against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Reliability is also paramount, with systems designed to withstand environmental factors and maintain consistent service, often incorporating redundant components and robust network management to ensure continuous operation.
Cost Insights for Satellite Internet Services
The cost of satellite internet services typically involves an initial equipment purchase or rental fee, followed by a recurring monthly subscription. Equipment costs can vary significantly depending on the provider and the technology generation (e.g., traditional geostationary vs. LEO systems). Monthly plans are often tiered based on speed and data allowances, with higher speeds or unlimited data plans generally costing more. Prices are estimates and can fluctuate based on market conditions, regional availability, and promotional offers. It is advisable for potential users to conduct independent research to compare current pricing and service packages available in their local services area.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (Equipment) | Cost Estimation (Monthly) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Service | Starlink | $599 - $2500 USD | $90 - $150 USD |
| Residential Plan | Viasat | $0 - $300 USD (rental/purchase) | $50 - $170 USD |
| Connect Plans | HughesNet | $0 - $450 USD (rental/purchase) | $65 - $160 USD |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The Future and Innovation in Satellite Internet Technology
The future of satellite internet is characterized by rapid innovation and expansion. Ongoing developments in satellite technology, including the deployment of larger LEO constellations and advancements in ground infrastructure, promise even greater speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. These innovations are set to further enhance the viability of satellite internet as a primary broadband solution, not just for remote areas but potentially for a broader range of users. The integration of satellite internet with mobile platforms and IoT devices also points to a future where ubiquitous, high-speed connectivity is more widely accessible, driving digital transformation globally.
Satellite internet continues to evolve as a critical component of the global digital infrastructure. Its ability to provide connectivity in challenging environments makes it indispensable for bridging the digital gap and fostering inclusive digital participation. As technology advances, satellite internet is poised to play an even more significant role in connecting the world and supporting a wide array of digital activities.