Understanding Different Cooking Methodologies
The art and science of preparing food involve a vast array of techniques, each designed to transform raw ingredients into delicious and digestible meals. From ancient traditions passed down through generations to modern innovations in the kitchen, understanding various cooking methodologies is fundamental for anyone interested in culinary practices. These methods do more than just cook food; they influence its texture, flavor, nutritional value, and overall appeal, playing a crucial role in global gastronomy and daily diet.
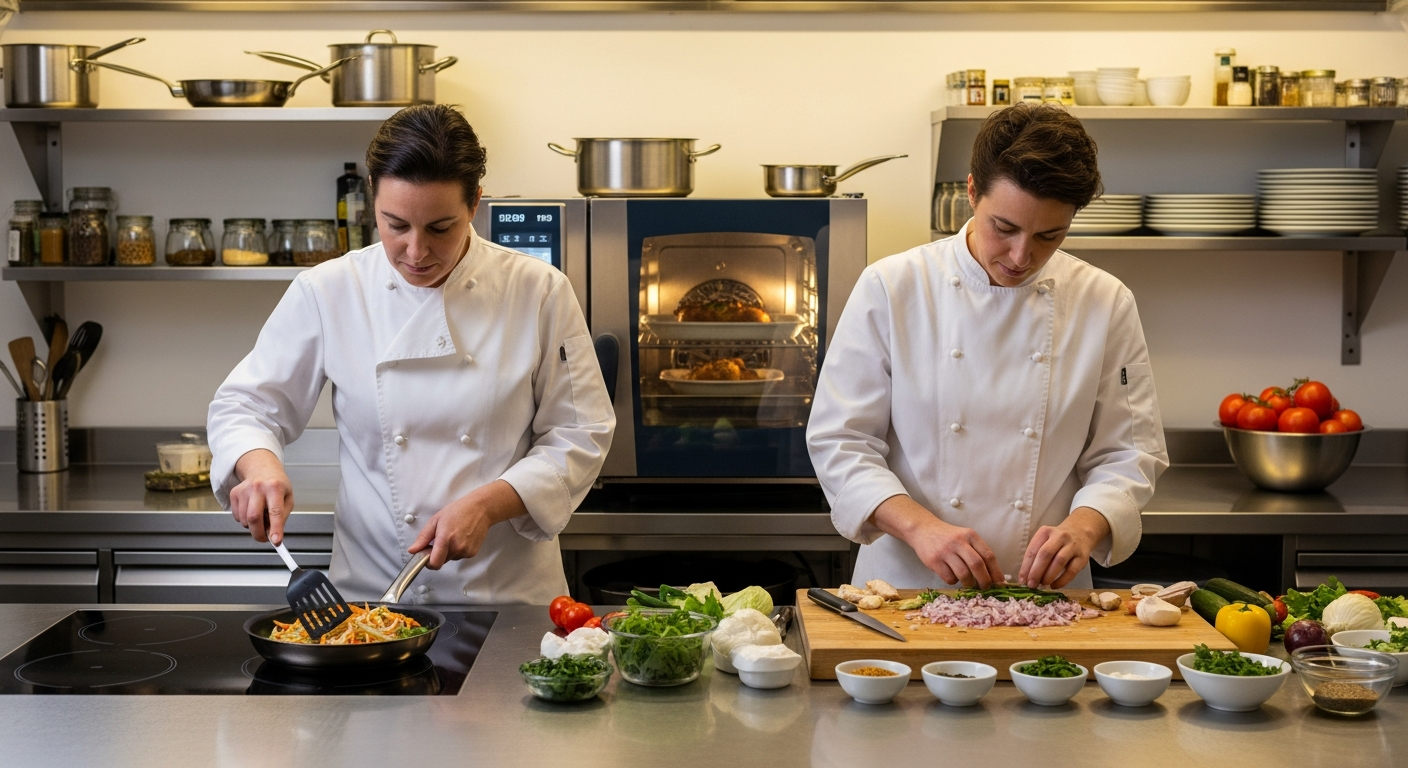

Cooking is a universal human activity, deeply intertwined with culture and daily life. The methodologies employed in food preparation are diverse, ranging from simple heat applications to complex chemical transformations. Each technique serves a unique purpose, affecting the final taste, texture, and nutritional profile of a dish. Mastering these methods allows for greater creativity and control in the kitchen, enabling home cooks and professional chefs alike to bring out the best in their ingredients.
Exploring Diverse Culinary Techniques
Culinary practices worldwide showcase an impressive array of cooking techniques, broadly categorized into dry-heat, moist-heat, and combination methods. Dry-heat methods, such as roasting, baking, grilling, and frying, involve cooking food without the addition of liquid, often relying on hot air, fat, or direct flame. These methods typically create a browned, crispy exterior and concentrated flavors. Moist-heat methods, including boiling, simmering, steaming, and poaching, utilize water or other liquids to cook food gently, often preserving moisture and delicate textures. Combination methods, like braising and stewing, begin with a dry-heat step (searing) followed by a moist-heat step (simmering in liquid), leading to tender, flavorful results, often found in traditional gastronomy.
Impact on Nutrition and Health
The choice of cooking methodology significantly influences the nutritional content and overall health benefits of meals. Some methods, like steaming and poaching, are known for preserving water-soluble vitamins and minerals that might otherwise leach into cooking liquids or be destroyed by high heat. Conversely, deep-frying can increase the fat content of food, impacting diet and wellness goals. Understanding how different cooking techniques affect nutrient retention and the formation of beneficial or detrimental compounds is key to preparing healthy food. For instance, quick stir-frying vegetables can retain more nutrients than prolonged boiling, contributing positively to a balanced diet.
Enhancing Flavor and Ingredients
Each cooking method interacts with ingredients in distinct ways, unlocking different flavors and textures. Roasting vegetables caramelizes their natural sugars, producing a sweeter, richer taste. Searing meat creates a Maillard reaction, developing complex savory flavors and an appealing crust. The precise application of heat and moisture can transform the raw produce, enhancing its inherent qualities. Understanding these interactions allows for intentional flavor development, transforming simple ingredients into memorable meals. The careful selection of a method can accentuate the freshness of ingredients or create entirely new taste experiences.
The Role of Cooking in Meal Preparation
Cooking methodologies are foundational to developing successful recipes and preparing satisfying meals. A recipe is essentially a set of instructions that guide the application of specific cooking techniques to a list of ingredients. Whether it’s the gentle simmering required for a delicate soup or the high heat needed for a crispy pizza, the chosen method dictates the outcome. Efficient meal preparation often involves selecting techniques that align with the desired texture, flavor, and time constraints, contributing to both culinary enjoyment and practical daily living. The right method can elevate everyday produce into something extraordinary.
Specialized Methods: Fermentation and Beyond
Beyond traditional heat-based cooking, specialized methods like fermentation play a vital role in culinary culture and food preservation. Fermentation, a metabolic process where microorganisms convert carbohydrates into alcohol or organic acids, is responsible for creating a wide range of foods and beverages, including yogurt, sourdough bread, kimchi, and kombucha. This process not only preserves food but also enhances flavor, texture, and often increases nutritional value by making nutrients more bioavailable. Hydration is also a critical aspect of many cooking processes, influencing everything from the texture of baked goods to the consistency of sauces and the preparation of various beverages.
Conclusion
The vast world of cooking methodologies offers endless possibilities for transforming food. From the ancient practice of open-fire cooking to the precise control of modern kitchen appliances, each technique plays a vital role in shaping our culinary landscape. By understanding how different methods affect ingredients, nutrition, and flavor, individuals can make informed choices, enhance their cooking skills, and appreciate the global diversity of food preparation. This knowledge empowers cooks to create delicious, healthful, and culturally rich meals, fostering a deeper connection to the food we consume and the traditions it represents.