Understanding Vehicle Aerodynamics for Efficiency
Vehicle aerodynamics plays a crucial role in determining a car's overall performance, particularly its efficiency. By managing the flow of air around and through a vehicle, engineers can significantly reduce drag, leading to better fuel economy for internal combustion engines and extended range for electric vehicles. This intricate field of automotive design directly influences how a vehicle moves through its environment, impacting everything from stability at high speeds to the amount of energy required to maintain momentum. Exploring the principles of aerodynamics offers valuable insights into the sophisticated engineering behind modern transportation.
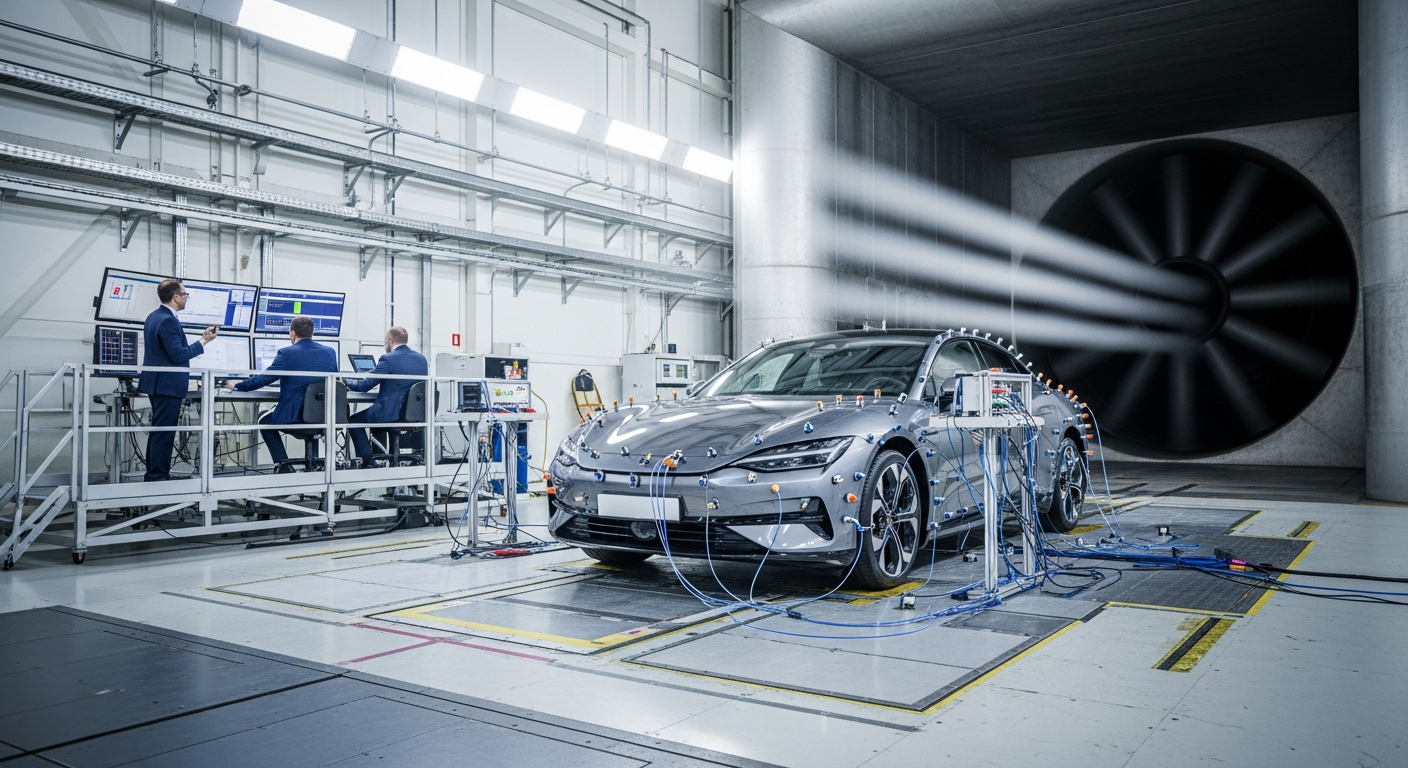

The concept of vehicle aerodynamics centers on minimizing air resistance, commonly known as drag, which opposes a vehicle’s motion. As a car or truck travels, it displaces air, creating pressure differences that can hinder its forward progress. Efficient aerodynamic design aims to smooth out this interaction, allowing air to flow over the vehicle with minimal turbulence and separation. This reduction in drag translates directly into less power required from the engine to maintain speed, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions for traditional vehicles, and greater range for electric models.
The Fundamentals of Vehicle Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, a branch of fluid dynamics, studies the motion of air and its interaction with moving objects. For a vehicle, the primary forces at play are lift, drag, and downforce. Drag is the most critical factor for efficiency, representing the resistance force exerted by air. It comprises form drag (due to the vehicle’s shape), skin friction drag (due to air rubbing against the surface), and induced drag (related to lift generation). Understanding these components is fundamental to designing a vehicle that cuts through the air effectively. Engineers use sophisticated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and wind tunnel testing to visualize and quantify these forces, iteratively refining designs to optimize airflow.
Aerodynamic Design Principles in Automotive Engineering
Automotive designers employ several key principles to enhance a vehicle’s aerodynamic profile. A streamlined shape, often characterized by a tapered rear and smooth transitions, is paramount to reducing form drag. Features like a sloped windshield, flush door handles, and integrated spoilers contribute to this streamlining. The underside of the car, often overlooked, is also critical; flat underbodies and diffusers can manage airflow efficiently, preventing turbulence. Furthermore, controlled airflow through the engine bay for cooling and around the wheels for stability are integral aspects of a comprehensive aerodynamic design. Each element, from the grille to the taillights, is meticulously crafted to guide air smoothly.
Impact of Aerodynamics on Fuel Efficiency and Electric Vehicle Range
The relationship between aerodynamics and efficiency is direct and substantial. For internal combustion engine vehicles, reducing aerodynamic drag means the engine expends less energy overcoming air resistance, leading to lower fuel consumption. This effect becomes more pronounced at higher speeds, where air resistance accounts for a larger proportion of total resistive forces. In the realm of electric vehicles, superior aerodynamic design is even more critical. A lower drag coefficient directly translates to an extended driving range, as less battery power is needed to maintain speed, thereby maximizing the usable energy stored in the battery. This makes aerodynamic optimization a cornerstone of the future of electric mobility.
Advanced Technologies for Aerodynamic Optimization
Modern vehicle technology incorporates numerous innovations to actively manage airflow. Active aerodynamic elements, such as adjustable spoilers, grilles that open or close based on cooling needs, and deployable air dams, can dynamically adapt to driving conditions. These systems can reduce drag at high speeds for efficiency or increase downforce for enhanced stability during performance driving. Vortex generators, strategically placed small fins, can also manipulate airflow to reduce turbulence. Furthermore, the integration of lightweight materials and advanced manufacturing techniques allows for more complex and efficient aerodynamic shapes without compromising structural integrity or adding excessive weight.
The Future of Aerodynamic Vehicle Design
The future of vehicle design is closely intertwined with continued advancements in aerodynamics. As the automotive industry shifts towards electric and autonomous vehicles, the emphasis on efficiency and range will only grow. Concepts like virtual design and active flow control will become standard, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in efficient and sustainable transportation.